

These nerves run through the canal and then out through their respective intervertebral foraminae. Pressure on the conus can cause impaired bowel and bladder control, and numbness around the anus and genitals (‘saddle anaesthesia’).īelow the ending of the spinal cord, the canal is occupied by the spinal nerves (also known as the ‘cauda equina’ which means ‘horses tail’, named after its appearance). The lower portion of the spinal cord is known as the ‘conus’ or ‘conus medullaris’. The spinal cord ends in the upper lumbar spine (usually at L1). As a result, pressure on these structures may occur.
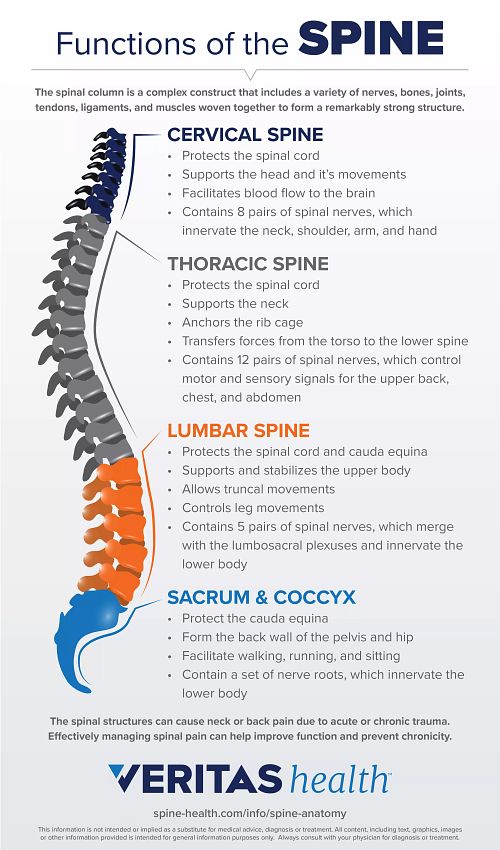
When the size of these tunnels is reduced, there is less room for the spinal nerves. The upper back, or thoracic spine, has 12 vertebrae, labeled T1. The spinal canal and intervertebral foraminae in the lumbar spine (lower back) are bony tunnels through which the spinal nerves (nerve roots) run. The top seven vertebrae that form the neck are called the cervical spine and are labeled C1-C7. Spinal nerves run through these compartments. The cervical spine supports the weight and movement of your head and protects the nerves exiting your brain. The area of the spinal canal immediately underneath the facet joint is known as the subarticular compartment or lateral recess. These units are the five different sections of the spine: The cervical spine the neck and upper back, composed of the seven vertebrae closest to the skull. Facet joints form part of the roof of the spinal canal. They allow movement between adjacent vertebrae and help to keep the spine stable. The facet joints are small joints on each side at the back of the spine. They are often removed (laminectomy) to decompress the nerves in the spinal canal.
#Sections of the spine skin
They meet in the midline, giving rise to the spinous process (the ridges that can be felt through the skin at the back of the spine). The laminae are ‘shingles’ of bone lying over the back of the spinal canal. It is the strongest part of the disc and it encloses the central nucleus and holds it under pressure to prevent it from rupturing. In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital. The annulus is a ring-like frame of fibres which connects each vertebral bone. The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column.It encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid.The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). There are no blood vessels or nerves in the nucleus, The rest of the nucleus is made up of connective tissue cells, collagen fibres, and a small amount of cartilage. It is a clear, jellylike material that is made up of 88 percent water in young adults.Īs the body ages and/or degenerates, the amount of water in the nucleus reduces. The nucleus functions as a primary shock absorber. The central soft and juicy nucleus is a sphere-shaped structure that allows tilting, rotating, and gliding movements in the spine. Each intervertebral disc has a strong outer ring of fibres (‘annulus’), and a soft, jelly-like centre (nucleus). A single disc sits between each vertebra. The intervertebral discs are soft structures which act as shock absorbers between each of the vertebrae (bones) in the spine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
